Every website we visit runs on a combination of two key building blocks: HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). These technologies work hand-in-hand to structure content and style its appearance. Whether it’s a simple personal blog or a complex e-commerce platform, HTML and CSS are always working behind the scenes. For anyone who wants to build, maintain, or understand a website, knowing how HTML and CSS function is not just useful—it’s essential.
What Is HTML and Why Is It So Important?
HTML is the backbone of any webpage. It tells the browser what content to display and how to organize it. Think of it as the skeleton of a building—it might not be flashy, but without it, the structure cannot stand.
HTML uses predefined tags to place elements like:
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Images
- Links
- Videos
- Buttons
- Forms
Each tag has a purpose. For example:
<h1>to<h6>are used for headings<p>is for paragraphs<img>adds an image<a>creates a hyperlink
Even though it’s simple in structure, HTML gives shape to everything on the web. A clean, well-organized HTML structure also makes it easier for browsers to read your content—and that plays a big role in performance and ranking.
What Is CSS and Why Does It Matter?
While HTML lays the groundwork, CSS is what gives your website style. CSS controls how things look: colors, fonts, spacing, backgrounds, animations, and layout. It takes the raw content from HTML and turns it into something visually appealing and user-friendly.
CSS allows developers to:
- Set a uniform font for the whole site
- Adjust the spacing between sections
- Make the background color dynamic
- Align content in columns or grids
- Add hover effects and animations
- Create responsive designs for mobile screens
Without CSS, every website would look like plain black-and-white text. CSS allows creativity, brand personality, and visual flow to shine through.
HTML and CSS Together: A Perfect Match
For instance, an HTML form might include input fields, checkboxes, and a submit button. But without CSS, that form would look awkward, unaligned, and hard to use. CSS steps in to align elements, add padding, define fonts, and even change colors on hover to improve user interaction.
Real-World Uses of HTML and CSS
Some practical examples where HTML and CSS shine together:
- Navigation Menus: HTML creates the menu items, and CSS styles them as dropdowns or horizontal bars.
- E-Commerce Product Cards: HTML structures the image, name, price, and button. CSS handles the layout, borders, shadows, and responsive behavior.
- Blog Layouts: HTML defines the article, author, and tags, while CSS makes sure each post is easy to read with proper margins and font sizes.
- Interactive Buttons: HTML defines the button element, while CSS adds colors, rounded corners, and animations.
Responsive Web Design with CSS
CSS plays a major role in making websites responsive. This means your site will look great on mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and desktops—without separate designs for each.
By using media queries in CSS, developers can set different rules depending on the screen width. For example:
- Use a single-column layout on phones
- Show a sidebar on tablets
- Display a full grid layout on desktops
Responsive design isn’t just a trend. It’s necessary. Search engines prefer mobile-friendly websites, and users expect smooth experiences on every device.
HTML5 – The New Standard
Modern websites benefit from HTML5, the latest version of HTML. It introduced many features that made web development more powerful and easier.
Some key additions in HTML5:
<section>,<article>,<nav>for better content organization<video>and<audio>tags to embed media without external plugins- Built-in form validation
- Improved accessibility and semantic meaning
These features not only make the code more readable but also help browsers and search engines understand your site better.
CSS3 – Styling with Power
Just as HTML5 brought new elements, CSS3 brought new styling capabilities. Developers can now create attractive animations and interactive effects with minimal code.
CSS3 adds features like:
- Transitions and animations for smooth visual effects
- Gradients for dynamic color changes
- Box shadows and text shadows
- Flexbox and Grid layout systems
- Custom fonts through @font-face
- Pseudo-classes like
:hover,:nth-child,:focusfor interactivity
These tools let designers craft highly interactive, engaging, and modern-looking websites without relying on JavaScript for everything.
HTML and CSS for SEO
A lot of people don’t realize that HTML structure directly affects SEO. Clean HTML code with semantic tags makes it easier for search engines to crawl and understand your content.
Here’s how HTML helps SEO:
- Use of
<title>and<meta>tags for better search listing <h1>,<h2>headings help define topic hierarchy<alt>attributes on images improve image search rankings<nav>,<header>, and<footer>help Google understand layout sections
A well-structured HTML layout supports faster indexing and higher chances of ranking better.
Accessibility with HTML and CSS
Accessibility is about making websites usable for everyone, including people with disabilities. HTML and CSS both contribute to this.
- Use semantic HTML so screen readers can navigate content properly
- Add aria-labels to describe elements
- Ensure color contrast in CSS for readability
- Use focus states for keyboard navigation
- Avoid using CSS to hide content that should be readable by assistive tools
Good accessibility improves user satisfaction and is becoming a legal requirement in many regions.
Easy Maintenance and Scalability
CSS allows websites to be maintained and updated easily. Instead of changing styles in every HTML file, you just update the CSS file once. This makes your code DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself) and efficient.
For large websites, using CSS classes and HTML templates ensures consistency across hundreds of pages. Developers can focus on content updates without worrying about layout or design breaking down.
The First Steps in HTML and CSS Coding
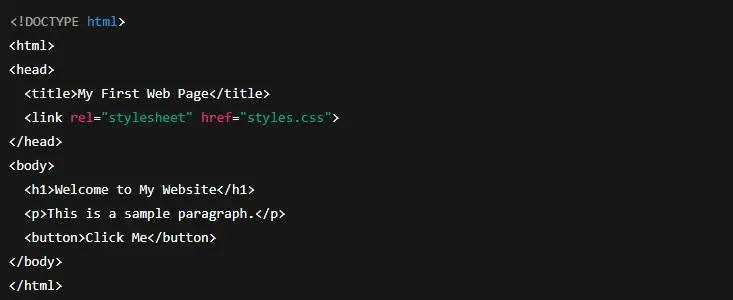
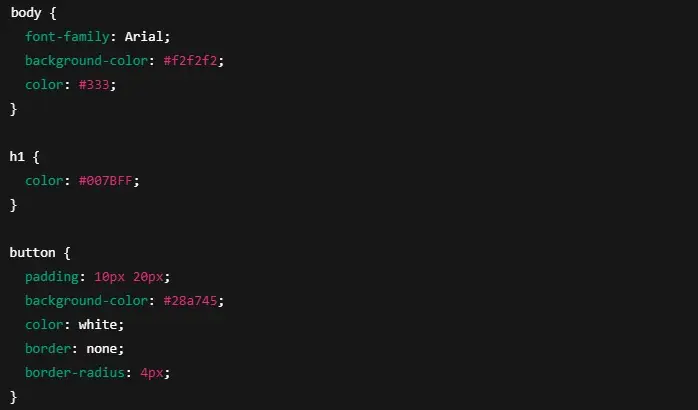
Getting started is easier than most people think. Here’s a basic example:
HTML
CSS
This simple structure gives you a functional web page with customized styles. From here, learners can expand into more complex layouts and features.
Why Businesses Should Care
A business website is often the first impression people get. Clean HTML ensures fast load times. Well-designed CSS creates trust and engagement. Together, they influence user behavior, from reading blog posts to completing purchases.
- Faster websites increase conversions
- Better design builds brand reputation
- Responsive layout means more traffic from mobile users
- Accessible websites reach more people
In competitive markets, these small details can set one business apart from another.
Final Thoughts
HTML and CSS are more than just coding tools. They form the foundation of the web. Every visually appealing, responsive, and high-performing website relies on these two technologies.
Even as frameworks like React or WordPress become popular, understanding HTML and CSS remains critical. They offer full control, better SEO, faster performance, and a deep understanding of how your site functions.
For anyone starting in web design, mastering HTML and CSS is not optional—it’s the smartest place to begin.